By Peninah Thande, Social Media Optimization Advisor, PSI Global; Stephen Maina, Program Manager, Social Media Optimization, PSI Global
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the world was not only fighting a highly infectious disease, but it was also up against another considerable challenge – misinformation. In July 2022, only 33.8 percent (9.2 million) of the adult population in Kenya was fully vaccinated. One of the main reasons people were not getting vaccinated was due to misinformation on social media.
To drive vaccine uptake, Kenya’s Ministry of Health (MoH) set a target to vaccinate 22 million Kenyans by the end of 2022.
In support of the MoH COVID prevention agenda, PS Kenya implemented a health behavior communication program intended to tackle vaccine hesitancy and reinforce COVID prevention practices. Funded through Unilever/Packard, with support from Meta, the program conducted a digital media campaign in the Kenyan counties of Nairobi, Kiambu and Mombasa because they the top 3 counties with the highest reported cases of COVID-19.1
Here is what we learned:
- The campaign was successful in reaching Kenyans with COVID-19 prevention communications focused on the importance of mask wearing and vaccinations. The campaign also reached 3.85 million people with clinic location services to get vaccinated.
- Message testing gave a clear indication on which creatives were likely to resonate better with the audience, for example use of real images instead of animations.
- Use of Swahili on the messaging and video creatives proved to be a success with a higher engagement rate witnessed in phase 2 (103%) compared to phase 1 (68%).
- Use of video was effective, leading to 2.5 million views with the highest engagement within the 25-34 age group which accounted for almost half of the total views.
PHASE 1: MASK WEARING AND VACCINE IMPORTANCE
The initial phase of the campaign, which primarily focused on the importance of wearing masks and getting vaccinated, utilized best practice digital marketing strategies to effectively communicate these messages.
The mask wearing messaging was primarily catered to younger audiences (age 18-24) because they were identified by WHO as a priority group in Kenya. In contrast, the vaccine importance messaging campaign focused on an older demographic aged 24-44 years because of their increased risk for COVID-related health complications and fear of taking the vaccine.
CREATIVE STRATEGY – MIXED APPROACH
The marketing campaign used an array of digital communication tools, including photo carousels, statics, and GIFS, to emphasize messages and offer the target audiences different means of exposure.


The campaign managed to reach 3.48 million Kenyan and reached more men (55.5%) than women (44.5%). It also had an impressive post engagement rate (amount of interaction the post received compared to it’s reach) of 52.66% compared to 2021 COVID-19 campaigns that saw an average engagement rate of 8.6%. The secondary audience (25-44 years) that were targeted with the vaccine importance messaging had a much higher engagement rate (109.73%) compared to the primary audience (56%).
BRAND LIFT STUDY
To assess impact, our campaign used the Brand Lift Study (BLS) measurement tool by Meta which measures outcomes from ad campaigns. The tool segmented a portion of our audience into two random groups: a control group who does not receive campaign ads and a treatment group who does receive campaign communications. Results of the Brand Lift study demonstrate the impact or “lift” our ads had on the treatment audience compared to the control audience.
For this campaign, we measured the following outcomes by asking control and treatment group members the following poll questions:
- Brand recall – Do you recall seeing an ad for PS Kenya online or on a mobile device in the last 2 days?
- Mask Wearing – In the last 2 days, how often did you wear a mask in public to slow the spread of the Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Vaccine Importance – How important do you feel a vaccine is to protect against COVID-19?
While achieving significant reach the campaign did not achieve a lift meaning there was no or limited change in the self-reported knowledge on mask-wearing and vaccine importance, among our target audience.
PHASE 2: ACCESS
After building awareness on the importance of COVID-19 prevention and vaccine importance, PS Kenya set out to promote vaccine access. This was done through digital messaging that directed Kenyans to the vaccine locator – a map of locations across Kenya to access the COVID-19 vaccine. An effective social and behavior change campaign must also connect our audience with the tools they need to take action.

The access phase of the digital marketing campaign incorporated learnings from phase one and resulted in the following changes to maximize reach and impact.
Swahili – To reach a wider audience, PS Kenya translated the campaign collateral into Swahili, the national language in Kenya.
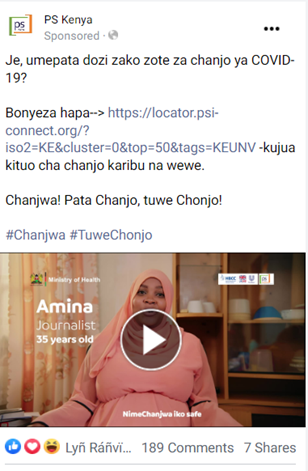

Video Messaging – To build on the success of using mixed creatives in phase one, the second phase incorporated video creatives to increase engagement.


MESSAGE TESTING
To ensure the campaign was effective in our target audience, we implemented A/B testing. This allowed us to test multiple creative elements in our messaging and design to determine which strategy leads to high engagement. For example, we tested the use of consumer images against images showing doctors as shown below.


PHASE 2 RESULTS
In terms of reach and engagement, the COVID-19 vaccine access campaign was a success. The access campaign reached 3.85 million people, 65% of which were male. There was also high campaign engagement within the target audience where they achieved an average click-through rate (CTR) of 3.2% (238,952 link clicks) well above the industry average of 0.11%.2. This high engagement was especially observed in the 35-44 age group.
Videos ads received a total of 2.5 million views, with the highest views primarily among the 25-34 age-group which accounted for almost half of the total views.
Our message testing through the A/B tests, also provided insights as to what creatives resonated with our audiences. Civilian creatives outperformed doctor creatives having achieved a lower cost per result ($0.021) as compared to the doctor creative ($0.023).
Real people creatives outperformed illustration creatives which had a lower cost per result ($0.016) as compared to illustration creative ($0.020).
While social media can be used as a weapon to drive COVID-19 misinformation, it can also be the key to challenging it. Digital media campaigns that work to provide consumers with reliable, accurate information and the resources to take action can be effective in addressing vaccine hesitancy and encouraging consumers to take COVID prevention measures.
What are the next steps?
PS Kenya together with the Ministry of Health is in the process of implementing the national-wide WhatsApp chatbot that will primarily be used to support vaccine information. The WhatsApp chatbot will incorporate learnings from this project.




















